2022
Jähnichen, S., Weber, F., Prentice, M., Lieder, F.
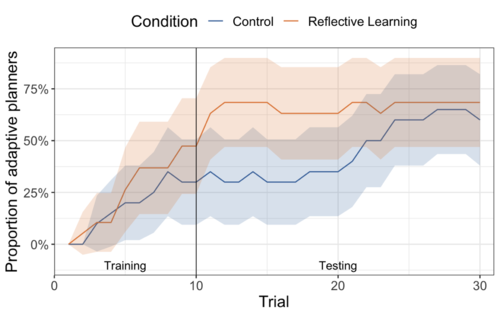
Does deliberate prospection help students set better goals?
KogWis 2022 "Understanding Minds", September 2022 (poster) Accepted
2021
Frederic Becker, , Lieder, F.
Promoting metacognitive learning through systematic reflection
The first edition of Life Improvement Science Conference, June 2021 (poster)
Lieder, F., Prentice, M., Corwin-Renner, E.
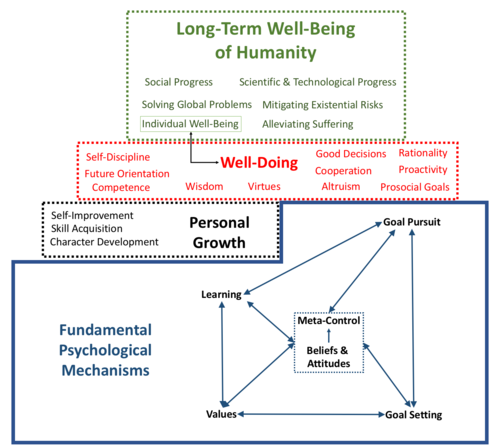
Toward a Science of Effective Well-Doing
May 2021 (techreport)
Consul, S., Stojcheski, J., Felso, V., Lieder, F.
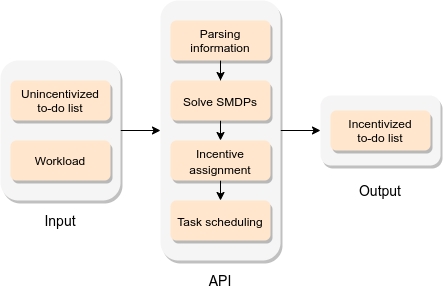
Optimal To-Do List Gamification for Long Term Planning
arXiv preprint arXiv:2109.06505, 2021 (techreport)
2020
Stojcheski, J., Felso, V., Lieder, F.
Optimal To-Do List Gamification
ArXiv Preprint, 2020 (techreport)